

Carmat aims to meet a major public health challenge related to cardiovascular diseases, namely heart failure, the leading cause of death in the western world. More specifically, Carmat aims to provide a lasting solution for the treatment of terminal heart failure, a disease for which there are very few effective options today, the main one being heart transplants.
From that date, CARMAT’s activities are thus transferred from CARMAT SA to CARMAT SAS, entity in which they carry-on.
However, CARMAT SA is due to be liquidated in the short-term and its shares will be delisted from Euronext Growth (Paris).
This website relates to CARMAT SA and will continue to be updated until the liquidation of the company becomes effective. Once the company is liquidated, all queries relating to CARMAT SA will have to be addressed to the liquidator who will have been designated.
Heart failure is a life-threatening condition in which the heart can no longer pump enough blood throughout the body.

Carmat
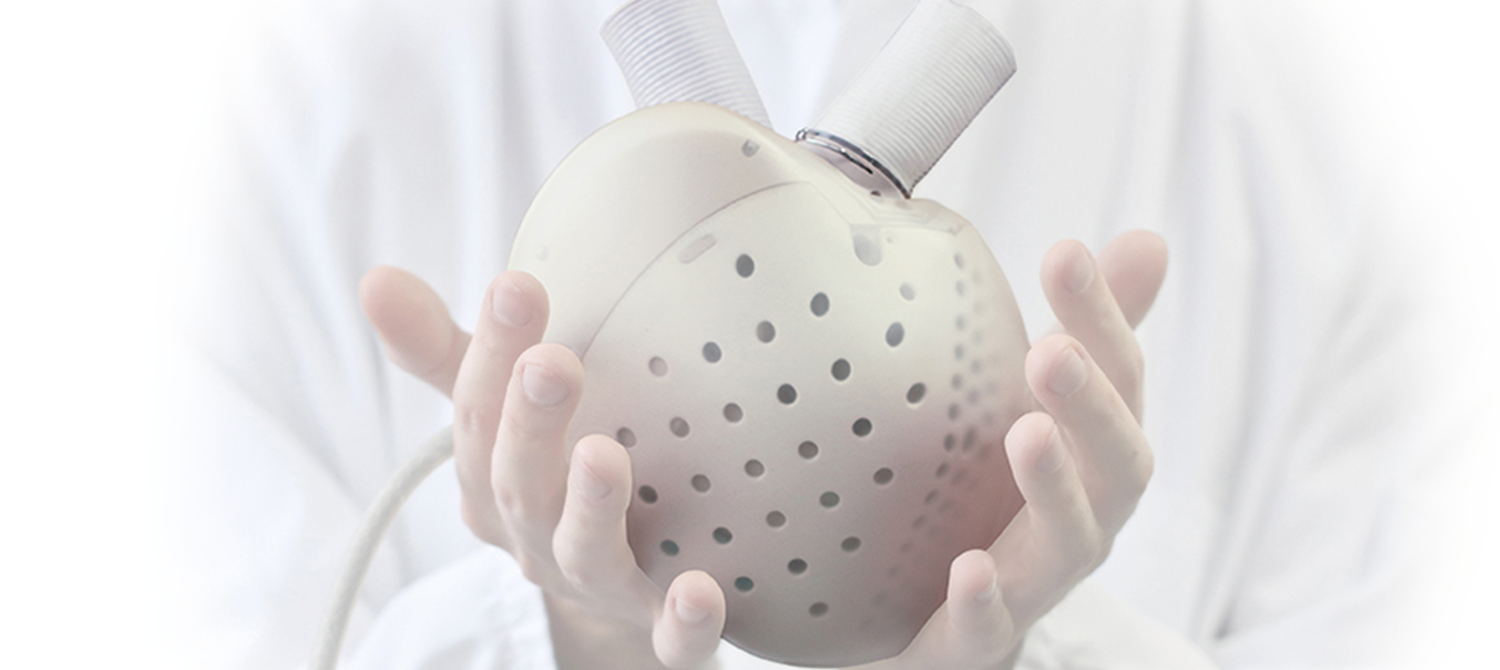
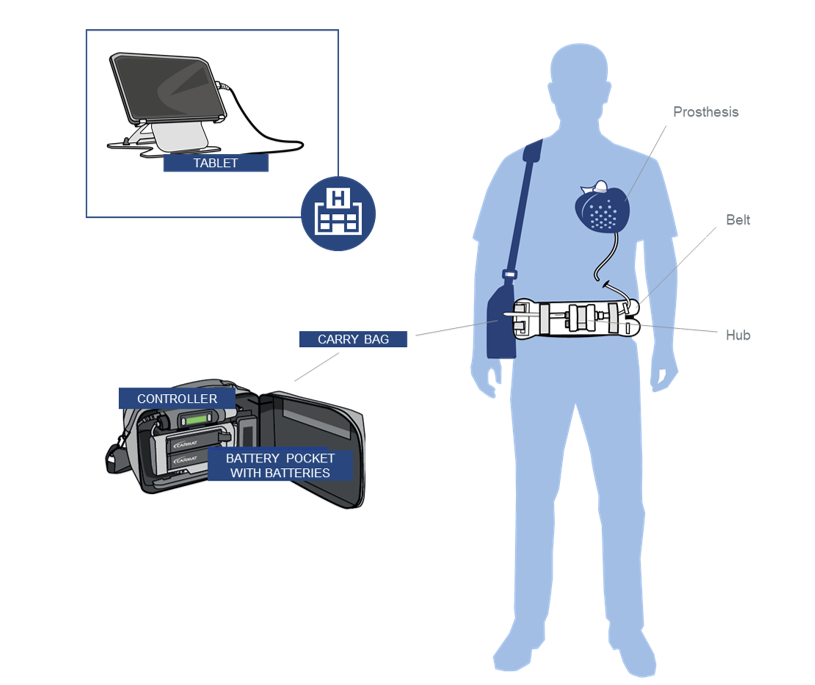
Aeson® Prosthesis with percutaneous driveline, mimics a natural heart in function and is powered and monitored by the External System.
The External System is defined as the external equipment contained in the Carry Bag and consists of a Controller, Battery Pocket with four
Batteries and a Patient Cable.
The External System provides the Patient with the mobility needed to lead a near-normal life.
Aeson® is an active implantable medical device intended to replace the ventricles of the native heart in patients suffering from advanced heart failure. The device is electro-hydraulically driven with a shape close to that of a human heart.
Once the Aeson® is connected, it duplicates the action of a normal heart, providing mechanical circulatory support and restoring normal blood flow through the body.
Aeson® is an active implantable device, commercially available in Europe ONLY, CARMAT SA, CE0344.
The Aeson® TAH is intended to replace ventricles. It is indicated as a bridge to transplant in patients suffering from end-stage biventricular heart failure (INTERMACS classes 1-4) who are not amenable to maximal medical therapy or LVAD and are likely to undergo heart transplant in the 180 days following device implantation. The decision to implant and the surgical procedure must be taken by Healthcare professionals trained by the manufacturer.
In the USA, Aeson® is currently exclusively available within the framework of clinical trials.
